Klinisk Biokemi i Norden · 4 2013
| 45
Even if the general setting for the actual ED does
limit the possibilities to address certain life-threate-
ning disease, mostly due to limited surgical capacity
for trauma, major bleed or neurosurgery, a limited set
of standard analyses will help the clinician to diag-
nose and accordingly treat immediate life-threatening
disease. These laboratory and radiological investiga-
tions could be labeled as life-saving samples and radio-
logy. Immediate life-threatening pathology includes in
order of the ABCDE-approach hypoxia and respiratory
insufficiency, shock and circulatory failure, coma,
unconsciousness and acute neurological impairment,
meningitis and sepsis, hypothermia and hyperthermia.
The potential acute life-threatening diagnoses related
to these symptoms can be found in table 1.
It should be kept in mind, that whilst a single labo-
ratory analysis might reveal the adequate diagnosis,
concurrent therapeutic options might rely on the
availability of supportive samples to guide the actual
therapy, as for example a D-Dimer and elevated tro-
ponins might be enough to determine the diagnosis
of severe pulmonary embolism, creatinine or cysta-
tin would alleviate the performance of a diagnostic
CT-scan, and aPTT and INR combined with Hb and
thrombocytes would be requested as minimum for a
therapeutic thrombolysis. As timely therapy on the
potential detection of a severe pulmonary embolism
(PE) requiring thrombolysis is essential, panel testing
on suspicion might be a reasonable option.
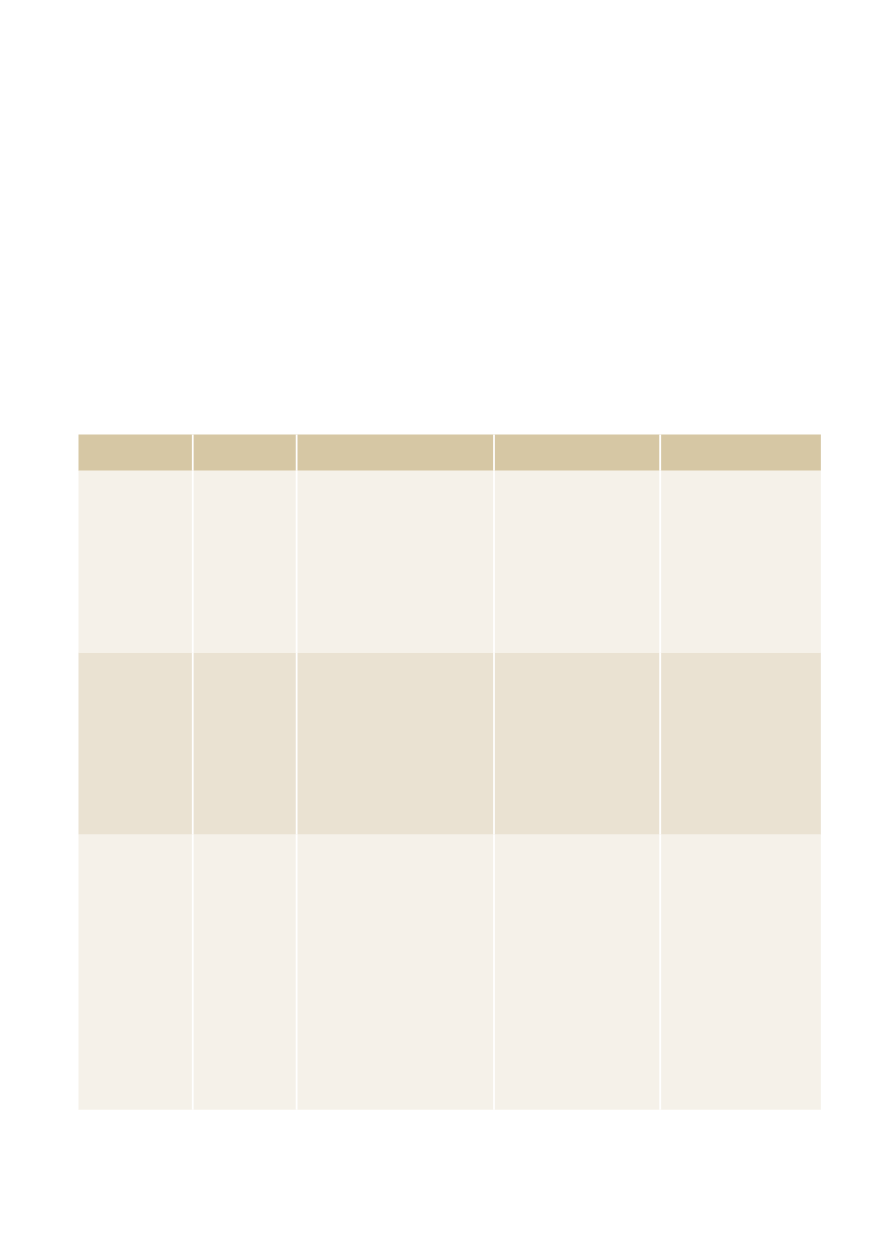
Symptom Diagnoses
Diagnostic laboratory Further laboratory
A (airway and
C-spine)
Impaired
airway
C-spine-
fracture
Trauma
Foreign body
Bleeding
Infection (epiglottitis, dip-
hteria)
Angiooedema
Tumor
Secondary loss of airway due
to coma
None. Clinical
diagnosis
CRP, WBC, creatinine,
INR, aPTT,
Hb, TPK
Preoperative:
ABG, Glucose,
electrolytes,
bloodgroup, Coomb’s
B (breathing)
Respiratory
insufficiency
Pneumothorax
Tensionpneumothorax
Pulmonary oedema
Asthma/COPD
Severe pulmonary embolism
Toxic
Neuromuscular insufficiency
Severe pneumonia
Massive pleural effusion
Arterial blood gases
(ABG)
D-Dimer
Troponin, LDH
Creatinine
Na, K
WBC, CRP,
aPTT, INR,
liver enzymes
osmolality
Liquorproteines
C (Circulation)
Shock
Bleeding
Hypovolemia
Cardiac tamponade
Arrhythmia
Anaphylaxis
Sepsis
Acute cardiac failure
Acute myocardial infarction
Endocarditis and valvular
problems
Endocrine insufficiency
(Addison’s, myxoedema)
Intoxication
Electrolyte disorders
ABG and lactate
Hb, TPK, WBC, CRP,
PCT
Na, K, ionCa,
Creatinine
Chloride and anionic
gap
S-Osmolarity
Troponin
INR
Urinary dipstick (blood,
nitrite, leucocytes)
aPTT
ASAT, ALAT
ALP
Bloodgroup
Coomb’s
Fibrinogen
D-Dimer
Elisa/PCR for infec-
tious agents


