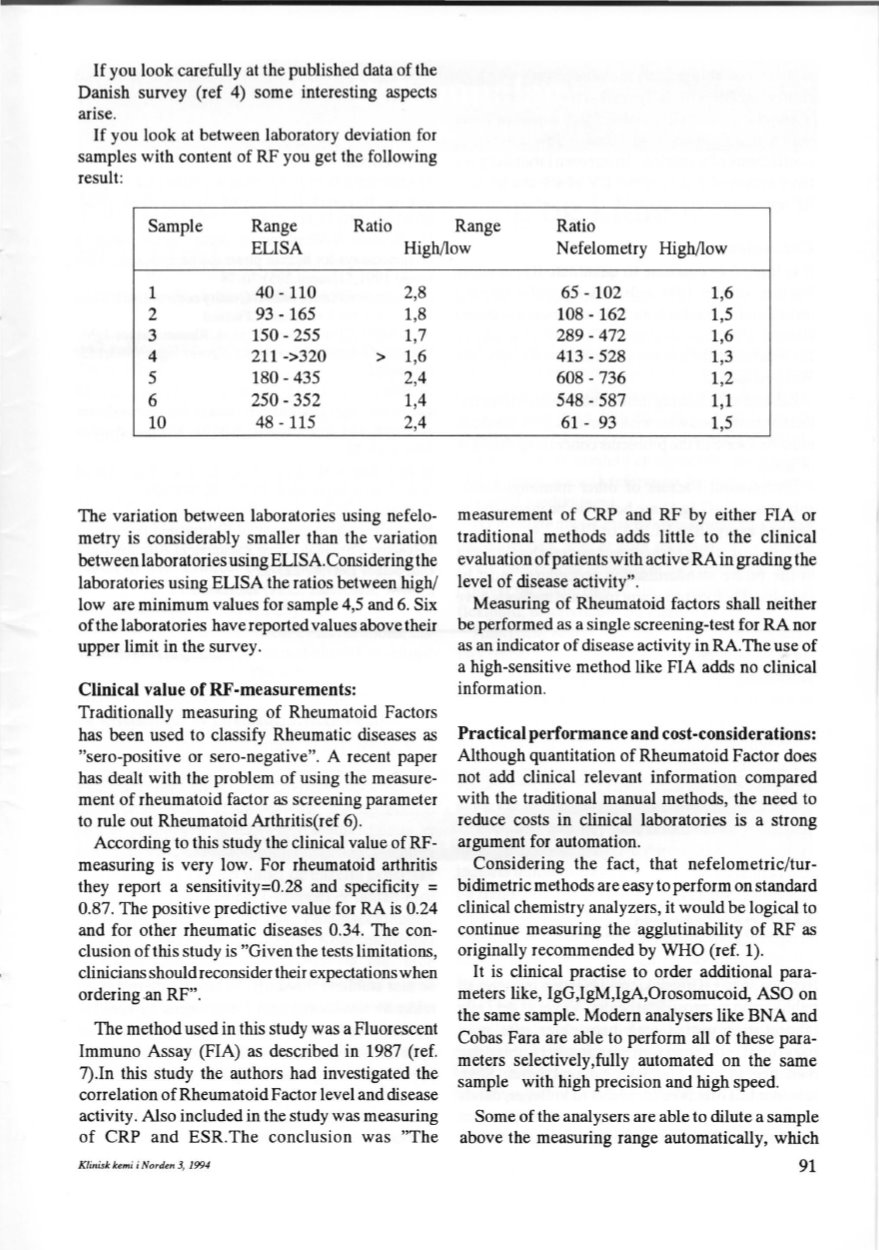
If
you look carefully at the published data of the
Danish survey (ref 4) some interesting aspects
arise.
If
you look at between laboratory deviation for
samples with content of RF you get the following
result:
Sample
Range
Ratio
Range
Ratio
ELISA
High/low
N
efelometry High/low
l
40-110
2,8
2
93- 165
1,8
3
150- 255
1,7
4
211->320
> 1,6
5
180-435
2,4
6
250- 352
1,4
10
48- 115
2,4
The variation between laboratories using nefelo–
metry is considerably smaller than the variation
between laboratories using ELISA.Considering the
laboratories using ELISA the ratios between high!
low are minimum values for sample 4,5 and 6. Six
ofthe laboratories have reported values above their
upper limit in the survey.
Clinical value of RF-measurements:
Traditionally measuring of Rheumatoid Factors
has been used to classify Rheumatic diseases as
"sero-positive or sero-negative". A recent paper
has dealt with the problem of using the measure–
ment of rheumatoid factor as screening parameter
to rule out Rheumatoid Arthritis(ref 6).
According to this study the clinical value of RF–
measuring is very low. For rheumatoid arthritis
they report a sensitivity=0.28 and specificity =
0.87. The positive predictive value for RA is 0.24
and for other rheumatic diseases 0.34. The con–
clusion of this study is "Given the tests limitations,
elinidans should reconsider their expectationswhen
ordering an RF".
The method used in this study was a Fluorescent
Immuno Assay (FIA) as described in 1987 (ref.
7).1n this study the authors bad investigated the
earrelation of Rheumatoid Factor leveland disease
activity. Also included in the study was measuring
of CRP and ESR .The conclusion was "The
Klinisk kemi
i
Norden 3, 1994
65- 102
1,6
108- 162
1,5
289-472
1,6
413-528
1,3
608-736
1,2
548- 587
1,1
61- 93
1,5
measurement of CRP and RF by either FIA or
traditional methods adds little to the clinical
evaluation ofpatients with active RA in grading the
level of disease activity".
Measuring of Rheumatoid factors shall neither
be performed as a single screening-test for RA nor
as an indicator of disease activity in RA.The use of
a high-sensitive method like FIA adds no clinical
information.
Practical performance and cost-considerations:
Although quantitation of Rheumatoid Factor does
not add clinical relevant information compared
with the traditional manual methods, the need to
reduce costs in clinical laboratories is a strong
argument for automation.
Considering the fact, that nefelometric/tur–
bidimetric methods are easy to perform on standard
clinical chemistry analyzers, it would be logical to
continue measuring the agglutinability of RF as
originally recommended by WHO (ref. 1).
lt
is clinical practise to order additional para–
meters like, IgG,IgM,IgA,Orosomucoid, ASO on
the same sample. Modern analysers like BNA and
Cobas Fara are able to perform all of these para–
meters selectively,fully automated on the same
sample with high precision and high speed.
Some of the analysers are able to dilute a sample
above the measuring range automatically, which
91


