S-Aibumin (BCG-method)
DIFF.ERENCE (measured - target) (g/L)
6
Centroi C Centroi A
;
1
f
accept limit
0
-r---~~a;~·~·±·E··~·±·t··~··~···~.·~···~
...
~
..
~--:~-:-~:·~:·:~·:
.....
····.······.·:
-2
accept limit
-4
-6
-8
-10
o
l
20
l
40
I
Centroi B
l
60
80
Target concentration (g/L)
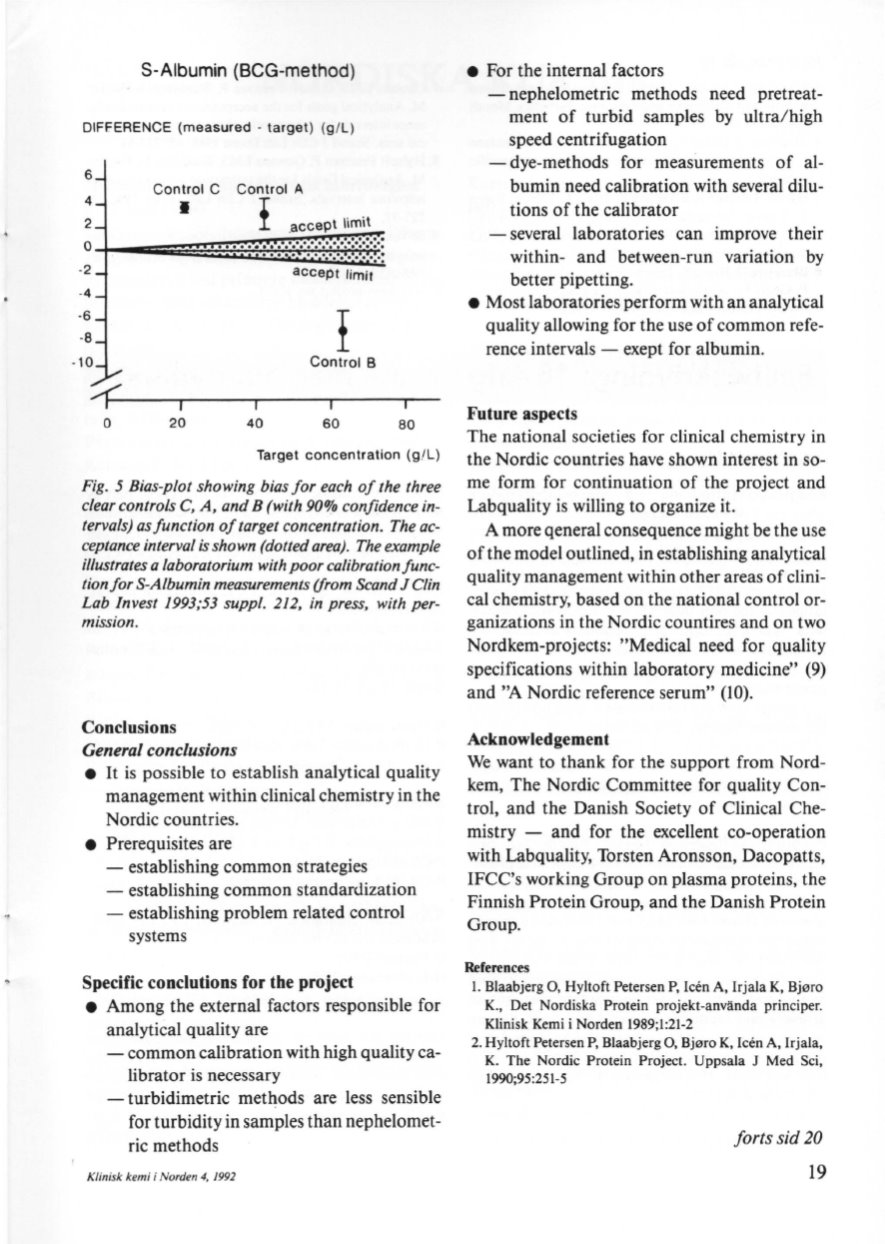
Fig. 5 Bias-p/ot showing bias for each of the three
e/ear contro/s
C,
A, and B (with 90% conjidence in–
tervals) as function oj target concentration. The ac–
ceptance interva/ is shown (dotted area). The example
illustrates a laboratorium with poor calibration func–
tion for s-Albumin measurements (from Seand
J
C/
in
Lab Invest 1993;53 suppl. 212, in press, with per–
mission.
Conclusions
General conclusions
e
1t is possible to establish analytical quality
management within clinieal chemistry in the
Nordie countries.
e
Prerequisites are
- establishing common strategies
- establishing common standardization
- establishing problem related control
systems
Specific conclutions for the project
e
Among the external factors responsible for
analytieal quality are
-common calibration with high quality ca–
librator is necessary
- turbidimetric methods are less sensible
for turbidity in samples than nephelomet–
ric methods
Klinisk kemi
i
Norden 4, 1992
e
For the intemal factors
- nephelometric methods need pretreat–
ment of turbid samples by ultra/high
speed centrifugation
- dye-methods for measurements of al–
bumin need calibration with several dilu–
tions of the calibrator
- several laboratories can improve their
within- and between-run variation by
better pipetting.
e
Most laboratories perform with an analytieal
quality allowing for the use of common refe–
rence intervals - exept for albumin.
Future aspects
The national societies for clinieal chemistry in
the Nordie countries have shown interest in so–
me form for continuation of the project and
Labquality is willing to organize it.
A more qeneral consequence might be the use
of the model outlined, in establishing analytieal
quality management within other areas of clini–
cal chemistry, based on the national control or–
ganizations in the Nordie countires and on two
Nordkem-projects: "Medical need for quality
specifications within laboratory medicine" (9)
and "A Nordie reference serum" (10).
Acknowledgement
We want to thank for the support from Nord–
kem, The Nordie Committee for quality Con–
trol, and the Danish Society of Clinieal Che–
mistry - and for the excellent co-operation
with Labquality, Torsten Aronsson, Dacopatts,
IFCC's working Group on plasma proteins, the
Finnish Protein Group, and the Danish Protein
Group.
References
l.
Blaabjerg O, Hyltoft Petersen P, Icen A, Irjala K, Bj0ro
K., Det Nordiska Protein projekt-använda principer.
Klinisk Kemi i Norden 1989;1:21-2
2. Hyltoft Petersen P, Blaabjerg O, Bj0ro K, Icen A, lrjala,
K. The Nordie Protein Project. Uppsala
J
Med Sci,
1990;95:251-5
forts sid 20
19


