49
| 3 | 2011
Klinisk Biokemi i Norden
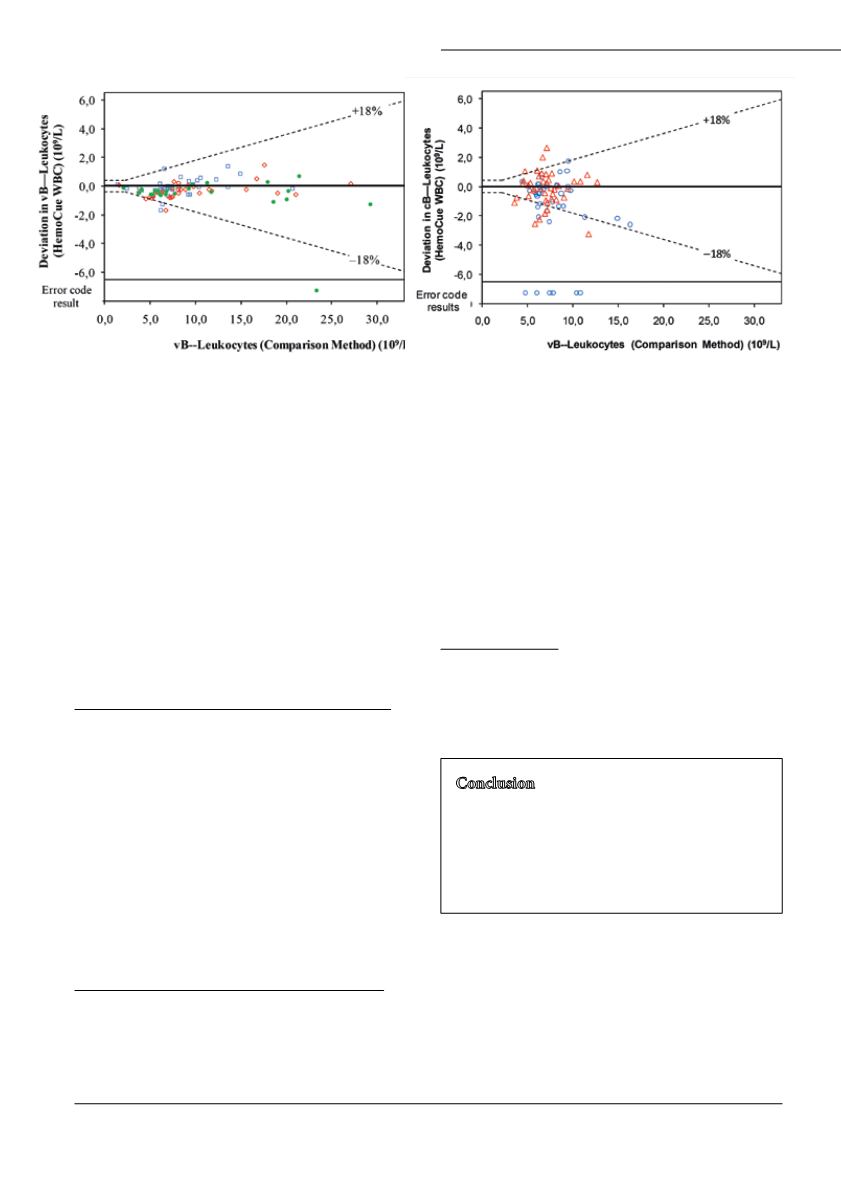
WBC results from venous samples almost fulfilled the
quality goal for bias.
Twenty samples containing atypical leukocytes
according the Advia cell counter was selected to
check the ability of HemoCue WBC to measure such
samples correctly. Almost all venous samples showed
good agreement between the HemoCue WBC and the
Advia results.
95%
of the results were inside the limits of ±18%, and
the quality goal for total error was fulfilled.
Venous samples at the primary care centres The
imprecision was similar to the imprecision in the
hospital laboratory, and the quality goal for precision
was fulfilled.
The bias of HemoCue WBC was estimated for the
results divided into two concentration level groups.
The bias for the low level group at the two primary
care centres was −16.0% and −12.1% respectively, and
for the high level group −6.1% and −5.4% respectively.
The quality goal for bias was only fulfilled for the high
level group. The samples in the primary care evalua-
tion were stored before measured with the comparison
method. This may have influenced the bias.
Capillary samples at the primary care centres The
agreement was not good when comparing capillary
HemoCue WBC results with results from the venous
comparison method. The imprecision for capillary
samples was 13.4% and 14.1% respectively at the two
primary care centres. The quality goal for bias was
fulfilled although the uncertainties in the estimates are
large. The storing time before the measurements with
the comparison method may have influenced the bias
as described for venous samples.
Seventy-seven percent of the capillary results were
inside the limits for total error.The HemoCue WBC
results did not fulfil the SKUP quality goal.
User-friendliness HemoCue WBC was regarded as
user-friendly and easy to handle. Short shelf life for
the internal quality control materials when unopened
is a drawback. The mean error code frequency for all
measurements in the evaluation was 1.6%.
Conclusion
For venous samples the analytical quality of
HemoCue WBC was good and fulfilled the quality
goals. However, for capillary samples the quality
goals were not fulfilled. HemoCue WBC was easy
to handle.
The complete report, SKUP/2010/73, with comments
and additional information from HemoCue AB, is
available at
Figure 2. Difference plot, venous samples in the hospital
laboratory
Figure 3. Difference plot, capillary samples in primary care


