16 |
Klinisk Biokemi i Norden · 2 2016
– sample” and the transported samples, and because
the biological and sampling variations are eliminated
as samples were drawn in the same puncture, the total
acceptable difference was defined as:
SD
2
Total acceptable deviation
=SD
2
Acceptable pre-analytical
deviation
+ 2 x SD
2
analytical
The quality demand was that at least 95.5 % of the
measurements had to be within 2SD
Total acceptable devia-
tion
from the “0 – sample”.
Statistics
Relative Difference plots are made with the relative
differences between the result from test sample and
“0 – sample” (part one) or the sample sent by the
first transport “0-sample” (part two and three) on
y – axis against time on x – axis. See appendix. The
limits for allowed deviation are shown in the plots.
The numbers of relative differences which fulfill the
allowed deviation in % are calculated.
Ethics
The Regional Danish Science Ethics Committee was
contacted by phone, and the Committee had no objec-
tions to this technical and quality investigation. Oral
informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Results
Part 1
Table 2 shows the maximal allowed deviation esti-
mated from the analytical CV, Clinical pre-analytical
deviation and critical level. We have decided that 95.5
% of the results shall fulfill the allowed deviation and
therefore use limits of allowable deviations as criteria
for transport from the GP’s to the laboratory without
preparation.
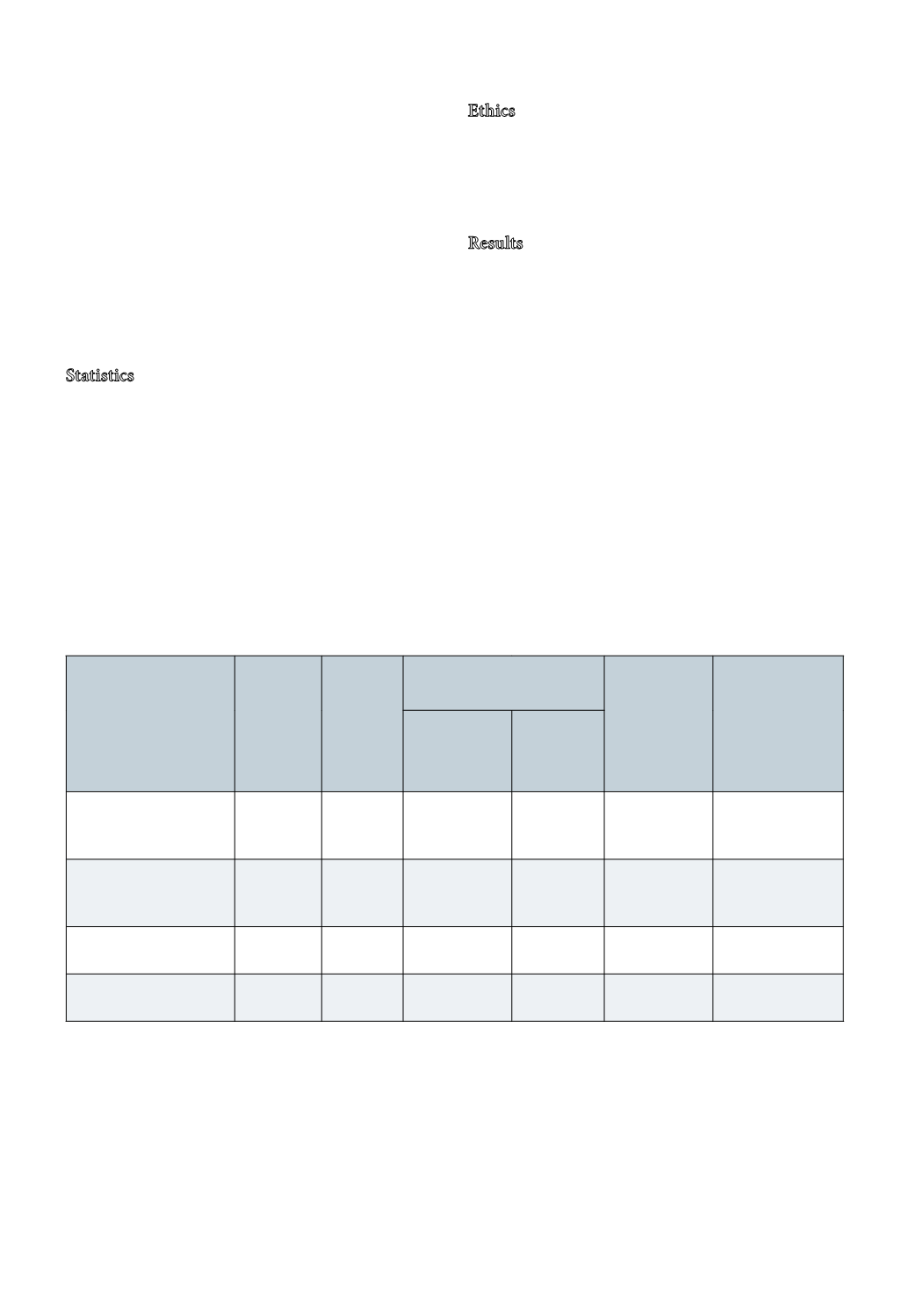
Table 2. Deviations from”0 – sample” which allows 95.5 % of the results to fulfill goals
Component
CV %
Analytical
Critical
level
Clinical pre-analytical
deviation*
Total CV for
deviation(%)
Allowed devia-
tion (%) between
0 – sample and
test sample
95.5% results
within ±2 SD
Concentration
CI 95.5 %
CV %,
Calcium – ion (pH
7,4)
mmol/l
2.0
1.3
0.2*
7.7
8.2
16.4
Prostate specific
antigen,
μg/l
3.8
4.0
1.0*
12.5
13.6
27.2
Parathyroid hormone,
pmol/l
9
7.0
1.0*
6.9
14.5
29.0
Proinsulin-C-Peptide.
pmol/l
5
130
50.2
23.9
24.4
48.9
Table 2: Critical level is the level at which the maximal allowed deviation is defined. Clinical acceptable pre-analytical devia-
tion (95.5% CI) is given as a concentration in reported units and as CV%. CV% analytical is the imprecision in the laborato-
ries. Total CV for deviation is the combined CV – analytical for both 0-sample and the test sample and the CV% of accepted
deviation. Maximal allowed deviation is the 95.5% CI limits for difference between 0-sample and test sample which fulfill the
goals at the critical level.
3
*Clinical acceptable pre-analytical deviation is an estimate


